In cooperation with Björn, it is splitted on "Disease is Different" into the sections by organ systems and combined with the real cases of our international testimonial / report archive of the related organ system.
KIDNEYS AND URETERS
The two bean-shaped kidneys, weighing approximately 120-200 g (4-7 oz) each, lie to the right and left of the spine behind the diaphragm. Their purpose is to filter blood plasma and make urine out of the residue. The kidneys regulate the body‘s water balance and acid-alkaline balance.
The actual filtering process takes place in the mesodermal kidney parenchyma. The renal cells (glomeruli) create 180-200 l (50 gal) of primary urine a day. Of this, 80-90% is reabsorbed in the renal tubules, which also belong to the kidney parenchyma.
Water is further removed in the endodermal kidney collecting tubules, so that only about 1% of the primary urine remains.
This amount, about 1.5 l (3 pt) per day, passes through the ectodermal renal pelvis, the ureter and the bladder (vesica urinaria) before being excreted.
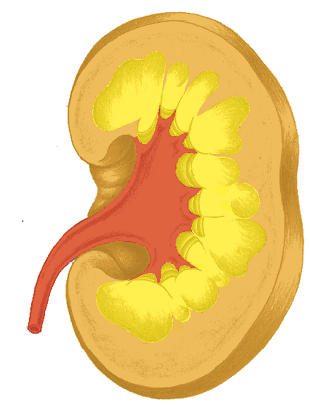
Kidney Parenchyma
Water/liquid conflicts
Kidney Collecting Tubules
Existential or refugee
conflict
Bladder
Territory-marking
conflict
Urethra
Territory-marking
conflict
Renal Pelvis/Ureter
Territory-marking conflict

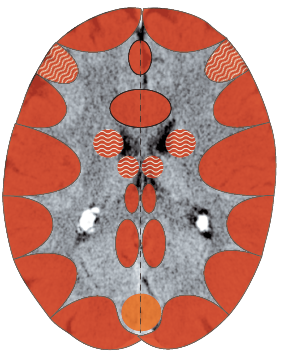
Fluid retention in the body, uremia, cancer of the kidney-
collecting tubules (adeno-ca)1
At a certain moments, every SBS is important, but if we had to name the most important SBS, then this is the one.
The significance of these little kidney tubules extends far beyond the kidneys themselves. All of the body’s other SBS are negatively influenced by an active SBS of the kidney collecting tubules and this is very important when it comes to therapy.
The repair phase of any SBS worsens if a kidney collecting tubules SBS is conflict-active, because of the increased accumulation of fluids. For instance, a repair phase crisis of the heart – a heart attack – can have dramatic consequences. In the case of a bone SBS (e.g., of the spine), this can lead to excruciating pain.
In the brain too, the pressure can become problematic if the healing Hamer focus is “pumped up“ due to an active kidney collecting tubules SBS.
The term “syndrome:“ Dr. Hamer came to call the simultaneous existence of an active kidney collecting tubules SBS along with another SBS in the repair phase a “syndrome.“ For instance, lower back pain (= repair phase of a central self-esteem conflict) + active kidney collecting tubules SBS = severe lower back pain, possibly a slipped disk.
When it comes to therapy for any syndrome, the resolution of the refugee conflict takes priority.
Inflammation of the renal corpuscles (“nephrotic syndrome,“ “glomerulonephritis,“ “IgA nephropathy“), multiple spaces (cystic kidney)
Same SBS as above (see: p.277).
The primary symptom for the conventional diagnosis is an excess of protein in the urine (proteinuria) or a protein deficit in the urine (hypoproteinuria) and fluid collection (edema).
It is said that with the so-called nephrotic syndrome, there is too little protein in the blood because the kidney‘s cell filtering apparatus is defective.
According to CM, this is why there is protein in the urine. In fact, this “illness“ is not an inflammation of the renal corpuscles but an inflammation, (i.e., the repair phase) of the kidney collecting tubules SBS.
| Phase | Repair phase or persistent repair: when the illness is chronic, there are repeating tubercular degradation phases – lots of small empty spaces in the kidneys (cystic kidney). |
|---|---|
| Note | Protein in the urine: During the repair phase, the kidney collecting tubules tumor is broken down . The protein removed is washed out in the urine through the bladder and ureter > protein in the urine (proteinuria). Too little protein in the blood: If the conflict comes back, the cell buildup and cell degradation phases in the kidney collecting tubules alternate. During tumor buildup, the body takes in protein (mainly albumin) from the blood. In the repair phase, it eliminates this tumor-protein again. Night sweats contains large amounts of protein > sinking of the blood protein levels (hypoproteinemia) > lower blood protein levels promote edema in the body due to a lessening of the colloid osmotic pressure. |
| Therapy | Determine the conflict and conditioning and if possibly resolve them in real life. Questions: see: p.279. Protein-rich diet and, if necessary, albumin infusions. The CM treatment, with drugs that lower the blood pressure, immunosuppressive drugs and cortisone, is not recommended. See also 279. |
Acute kidney failure, shock kidney (acute ischemic tubulopathy)
| Example |  A 49-year-old farmer is going through a very difficult time: His wife divorced him and left him, taking their two daughters with her. He was left sitting at home alone on a mountain of debt = acute existence conflict. Diagnosis: acute kidney failure. For 18 months, he had to go for dialysis several times a week. Through incredibly hard work, he managed to pay off his debts and he meet a new partner = resolution of his existence conflict. His blood counts showed continued improvement and he no longer needed dialysis. With a very healthy diet and a lot of natural medicine, he was able to keep himself healthy. 22 years later, his creatinine level suddenly rose up to 3.9 again – When his daughter, now an adult, got a divorce = relapse based on the sympathy he feels for his daughter. (Archive B. Eybl) A 49-year-old farmer is going through a very difficult time: His wife divorced him and left him, taking their two daughters with her. He was left sitting at home alone on a mountain of debt = acute existence conflict. Diagnosis: acute kidney failure. For 18 months, he had to go for dialysis several times a week. Through incredibly hard work, he managed to pay off his debts and he meet a new partner = resolution of his existence conflict. His blood counts showed continued improvement and he no longer needed dialysis. With a very healthy diet and a lot of natural medicine, he was able to keep himself healthy. 22 years later, his creatinine level suddenly rose up to 3.9 again – When his daughter, now an adult, got a divorce = relapse based on the sympathy he feels for his daughter. (Archive B. Eybl) |
|---|---|
| Phase | Sudden strong existence conflict: extreme water and urea storage > strong rise in creatinine and urea values, very little urine (oliguria or anuria). |
| Note | Usually caused by extreme pain, diagnostic shock or forced admission to a hospital. |
| Therapy | Identify the conflict and conditioning and, if possible, resolve them in real life. For measures, see above, especially Prof. Kopp’s therapy. |
1 See Dr. Hamer, Charts p. 25

Kidney tumor (Wilms‘ tumor, nephroblastoma), kidney
cavity (kidney cyst)1
| Conflict | Liquid conflict, conflict due to too much water or liquid, conflict when liquids or water becomes dangerous, “non-swimmer-in-the-sea“ conflict. |
|---|---|
| Examples |  A man comes home and discovers, to his dismay, that the basement is full of water, because the washing machine‘s intake hose burst. = Liquid conflict > cell degradation in the parenchyma of the kidneys during the active–phase, restoration or growth of a tumor in the repair phase. (Archive B. Eybl) A man comes home and discovers, to his dismay, that the basement is full of water, because the washing machine‘s intake hose burst. = Liquid conflict > cell degradation in the parenchyma of the kidneys during the active–phase, restoration or growth of a tumor in the repair phase. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman‘s beloved cat drowns in the swimming pool. She finds the animal floating lifeless in the water. = Liquid conflict. Three years later, a nephroblastoma is discovered by chance. She is advised to have chemotherapy at once. The woman dies. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman‘s beloved cat drowns in the swimming pool. She finds the animal floating lifeless in the water. = Liquid conflict. Three years later, a nephroblastoma is discovered by chance. She is advised to have chemotherapy at once. The woman dies. (Archive B. Eybl) The “Case: Olivia” Olivia’s aunt took her out on a lake in an inflatable boat. Her aunt suddenly noticed that the boat was leaking air, so she screamed in a shrill voice: “Help! Help! We’re going to drown!” Olivia believed she was going to drown within the next few minutes = liquid conflict. > Necrosis in the active phase, cell growth in the repair phase. She was diagnosed with a Wilms’ tumor. (Cf. Helmut Pilhar, Olivia – Tagebuch eines Schicksals p. 564) The “Case: Olivia” Olivia’s aunt took her out on a lake in an inflatable boat. Her aunt suddenly noticed that the boat was leaking air, so she screamed in a shrill voice: “Help! Help! We’re going to drown!” Olivia believed she was going to drown within the next few minutes = liquid conflict. > Necrosis in the active phase, cell growth in the repair phase. She was diagnosed with a Wilms’ tumor. (Cf. Helmut Pilhar, Olivia – Tagebuch eines Schicksals p. 564) A woman suffers from severe incontinence = too-much-liquid conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman suffers from severe incontinence = too-much-liquid conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman, now 40+, is five years old when she suffers a liquid conflict while playing A woman, now 40+, is five years old when she suffers a liquid conflict while playing with other children on the bank of a river. Suddenly, she slips into the water and is carried away by the current. Fortunately, an older playmate pulls her onto land again, but she remembers those terrible moments to this day. In the active–phase, a “hole“ forms in her kidney; in the subsequent repair phase, a 10 cm (3 in) cyst forms, which hadn‘t caused her any problems for 40 years. Note: the patient is “sensitized“ to the liquid conflict, because as an unborn child she came into danger in high water “with her mother.“ Since the water had already flooded the whole lower floor of the house, the pregnant mother had to flee to the attic = liquid conflict. (See Claudio Trupiano, thanks to Dr. Hamer, p. 420) |
| Conflict-active | Cell degradation (necrosis) in one or more places > loss of kidney parenchymal (basic) tissue > in order that the filtering function continues unchanged, the organism raises the blood pressure = “compensatory hypertonia.“ The necroses are otherwise not noticed. |
| Repair phase | Out of the holes resulting from cell destruction, one or more fluid-filled kidney cysts develop (CM: “polycystic nephropathy“ or “renal dysplasia“). In the course of time, the cysts are gradually filled out with functional kidney tissue. After nine months, an “additional“ kidney has formed, with its own arteries and veins, etc. Connections to the neighboring organs (CM = “invasive growth“), having been necessary for the cyst’s own blood supply, dissolve when the cyst’s own circulatory connection is complete. In this “additional kidney,“ blood is filtered just like in the rest of the parenchymal tissue. The increased blood pressure is then superfluous > normalization of the blood pressure toward the end of the repair phase. |
| Bio. function | Increase in the filtering and urine-making capacity; in the future, an excess of water can be handled better (luxury group). |
| Note | There is no need to differentiate between the mother/child and partner side. “Handedness” is immaterial. |
| Questions | Determine the phase based on the symptoms (blood pressure, ultrasound, x-rays, general indicators). Which stress was experienced with water or other liquids? (Seaside vacation, water sports, kitchen/bath or work accident, sympathy with drowning victim(s))? What has conditioned me with regard to water? (E.g., childhood experiences – shoved into water, ancestors)? How could I come to terms with/reconcile this conditioning? How can I change the situation in real life? |
| Therapy | The conflict is resolved. No measures need to be taken, except to prevent recurrences. If the nephroblastoma is so large that it disturbs other organs, surgery is recommended – preferably after nine months, so that the tumor has had time to form its own circulatory system and has detached from its neighboring organs. In the case of complications due to lack of space, one should only continue to “wait it out” if they are absolutely sure that the conflict has been permanently resolved. |
1 See Dr. Hamer, Charts pp. 69, 81
Inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis), cancer of the renal pelvis1
| Conflict | Territorial-marking conflict. The territorial borders are not being respected, one cannot mark them. Explanation: Not being able to distance oneself from someone/thing or delineate one’s territory. Not knowing where one‘s territory (place) is. Not having the confidence to make a decision or not being allowed to make a decision oneself. In nature, the male wolves mark the outer and the females mark the inner borders of the territory. With men, it is usually about the “outer” territory (the job, car, club, etc.). With women, it is usually about the “inner” territory (partner, child, friend, home, etc.). In Lexikon der Neuen Medizin, Horst Köhler points out that the woman‘s most intimate territory is her own body. Gynecological examinations, involuntary or “tolerated“ sexual intercourse could be one reason why women suffer from urinary illnesses more often than men. The right renal pelvis or ureter > “feminine“ side = conflict of not being able to mark the inner territory. The left renal pelvis or ureter > “masculine“ side = conflict of not being able to mark the outer territory. |
|---|---|
| Examples | ➜ Not knowing where one should draw the line, not knowing how to define oneself. ➜ A child doesn‘t have his own room.  A woman is cheated on by her husband = territorial-marking conflict > unnoticed cell degradation in the renal pelvis. As she finally decides to leave him, she comes into the repair phase > restoration of the squamous epithelium of the renal pelvis = pyelonephritis. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman is cheated on by her husband = territorial-marking conflict > unnoticed cell degradation in the renal pelvis. As she finally decides to leave him, she comes into the repair phase > restoration of the squamous epithelium of the renal pelvis = pyelonephritis. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman marries into a family in which she does not feel right. She doesn‘t know where her place is. She no longer has her “own realm“ = territorial-marking conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) A woman marries into a family in which she does not feel right. She doesn‘t know where her place is. She no longer has her “own realm“ = territorial-marking conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) A salesman has a part of his sales area taken away, because he is not making enough sales = territorial-marking conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) A salesman has a part of his sales area taken away, because he is not making enough sales = territorial-marking conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Conflict-active | Degradation (ulcer) of the mucosa in the renal pelvis, renal calyxes or ureter (urothelium). Increased urge to urinate. No pain; therefore, usually unnoticed. |
| Bio. function | Through the relaxed ring musculature, the cross-section increases. > Improved elimination of urine so that the territory can be marked better. |
| Repair phase | Restoration of the urothelium, inflammation of the renal pelvis (possibly “cancer” of the renal pelvis as defined by CM), swelling, and blood in the urine (hematuria). With syndrome, the flow of urine can be impeded by repair swelling. |
| Repair crisis | Cramps, kidney colic, severe pain, chills, blood in the urine; during the colic (contractions of the ureter muscles) kidney gravel or calyx stones are pressed through the neck of the renal calyx into the renal pelvis or through the ureter, if they are present. |
| Questions | Inflammation/pain since when? (Conflict resolution shortly before) Which territory was I unable to mark before? Did someone overstep the boundaries? (Partner, family member, place of employment, superior)? Was I unable to bring someone into my territory? (With women, this usually concerns their partner). Was my “No!” ignored/overruled? Why do I react so sensitively? (Determine the precise conditioning). Do I react similarly to my ancestors? Which new attitude could help? |
| Therapy | The conflict is resolved. Support the healing. If it returns, identify the conflict and/or trigger(s) and resolve them. Guiding principle (if recurring): “I have decided. Now I know what I want.“ “My territory is my realm.“ “I define the borders and they will be respected.“ Teas: sage, cranberry leaves, rose hip, lovage, horsetail. Colloidal silver internally. Drink a lot, e.g., natural beer. Antibiotics if necessary, if the repair phase is too intense. See also: remedies for the kidneys p. 285. |
Enlargement of the renal pelvis, sacculated kidney (pyelectasis, hydronephrosis)
Same SBS as above.
| Phase | Persistent repair: Enlargement of the renal pelvis or the ureter, usually in connection with kidney stones > necrosis of the parenchymal tissue of the kidneys (narrowed parenchyma-seam) caused by blocked urine flow. |
|---|---|
| Therapy | Identify the conflict and conditioning and, if possible, resolve them in real life, so that the persistent repair can come to an end. Questions: see previous page. See also: remedies for the kidneys p. 285. |
1 See Dr. Hamer, Charts pp. 117, 130

Renal artery stenosis (increased blood pressure from narrowed kidney arteries)
The narrowing of the main vessels leading to the kidneys means less blood reaches the kidneys. > Erroneously, the blood pressure receptors in the kidneys register low blood pressure > impulse to increase blood pressure (RAS) > increase in blood pressure (possibly acute), dizziness, morning headaches, possible lung edemas (shortness of breath).
| Conflict | According to Dr. Sabbah: One is boiling with anger on the inside and can’t let off the steam. One feels worthless because of chronic existential problems (kidney collecting tubules). Issues of family, blood ties, total loss: demise of the bloodline. |
|---|---|
| Example | ➜ “My kidney values are extremely bad; how long will they continue to function?” |
| Phase | Recurring–conflict. Alternating phases of depletion and restoration of the renal arteries results in the formation of a fatty-protein material > CM: “renal arterial sclerosis/stenosis.” |
| Bio. function | Strengthening of the renal arteries. Persistent conflict and the resulting narrowing of the arteries doesn’t make any biological sense – nature is always assuming that conflicts will be resolved quickly. |
| Questions | Why am I angry? Why don’t I let it out? Which conditioning is responsible? |
| Therapy | Determine and resolve the conflict, causal conditioning and beliefs. OP if necessary. |

Congenital ureteral stenosis or malformation
A relatively common early childhood disease/developmental disorder.
| Conflict | Devaluation conflict inherited from ancestors (= substitute conflict), that the territory is too small/narrow. Constriction of freedom/possibilities. |
|---|---|
| Example | ➜ “My territory is restricted.“ a In the 22nd week of pregnancy, the unborn child is diagnosed with a ureteral stenosis. The flow in the left ureter is reduced by 50%, the renal pelvis is enlarged (congested kidney). History: the boy is the second-born (looks to the mother). The main parental issue: the mother has the urge to go out and explore, wants to experience something, but the father prefers to stay at home. The older daughter demanded a lot from the mother and is now also jealous of the little brother. The mother is alone at home and has no more free time/freedom. “My territory is small and narrow.” This emotion is a generational theme: The mother’s father has an unbridled desire for freedom. Two marriages have already failed because of this and his partners’ very high expectations. The signal to the little one: “Because of restricted freedom, mom and dad could separate. I should constrict the ureter – that will suit my mom’s small territory. After the cause is discovered in conversation with the therapist, the following “therapy” is decided upon: 1. The mother should talk to her husband again about how important it is for them to go on trips together, so that she can feel free again. 2. She should also discuss this topic with her father (which would also be healing for him). 3. She should meditate regularly: “I feel free, even if I have some obligations.” 4. While rocking her son to sleep, she should thank him for carrying and pointing out this issue for her. Then she should to tell him that she is happy with dad now, because she can experience her freedom now, they will stay together and all is well. Three months later, the check up at the hospital shows that her son’s ureter has clearly dilated (normalized). The planned surgery is postponed – they want to give the positive development a chance. (Archive B. Eybl) (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Phase | Persistent substitute conflict. Scarring shrinkage of the affected ureteral area. The constriction prevents urine from flowing properly, possibly backing up. If the back-up is prolonged, the renal pelvis dilates and impairs kidney function. If the issue remains unresolved/the stenosis untreated, kidney tissue may atrophy. |
| Bio. function | Revealing the family issue. The territory is small/narrow, so that little urine is sufficient for marking. |
| Therapy | Identify the inherited ancestral issue (look for it among parents, grandparents) and resolve it (see chapter: Conditioning on p. 27ff and chapter: Therapy on p. 52ff) . The “family waltz” (see p. 30) gives clues to whether the cause lies on the mother’s or father’s side. Guiding thoughts: “I gratefully accept the obligations I have voluntarily entered into, for they are in harmony with my soul’s mission – seen in this light, my territory is vast.” “True freedom comes from recognizing and placing oneself in the divine order.” Without significant symptoms (congested kidney), CM treatment (surgery) is not necessary, especially since the stenosis usually improves as the child gets older. |
Kidney stones (nephroliths), kidney gravel
Possible causes
• Kidney collecting tubules – Recurring refugee conflict: calcium oxalate stones and/or gravel as mineral deposits from tubercular caseation = the most common kind of kidney stones (see: p.277).
• Ureter and/or mucosa of the renal pelvis – Recurring territorial-marking conflict: uric acid stones and other stone types; healing swelling of the ureter > occlusion or flow blockage > damming of urine leading to sediment deposits and the formation of stones. In the course of a repair phase crisis, the stones are forced out through the ureter or urethra (see: p.282).
Therapy
Identify the conflict and/or trigger(s) so that no new stones form. Dissolution by “Lithosol“ (minerals, by prescription). If necessary, surgical stone removal or lithotripsy. Drink sufficient, pure, “soft“ water. See also: remedies for the kidneys next page.
Cirrhotic kidney
Possible causes
• Kidney parenchyma: Recurring (= persistent) liquid conflict. Demise of the basic tissue of the kidney – converts to connective tissue (fibrosis). > Reactionary increase in blood pressure due to lack of filter surface (see: p.281).
• Kidney collecting tubules – Recurring refugee conflict – nephrotic syndrome > scarred shrinkage (see: p.277).
• Renal pelvis – Recurring territorial-marking conflict > chronic inflammation of the renal pelvis > scarred shrinkage (see: p.282).
Kidney poisoning (acute toxic tubulopathy)
This is not a conflict; rather, it is a poisoning by chemicals, metals (e.g., aluminum, mercury and other metals e.g., in vaccinations, chemtrails) and/or medications (antibiotics, painkillers, antirheumatics, antihypertensives, contrast agents, chemotherapeutic drugs, etc.). > Damage to the renal cells and tubules. See also Acute kidney failure p. 280
Therapy
Eliminate exposure to toxic substances. Also, see remedies for the kidneys.
Ureteral stenosis (ureter narrowing), uteropelvic junction (UPJ) stenosis
Usually the narrowing is discovered by ultrasound when looking for the causes of urine retention in the kidney.
Possible causes:
• Injury scarring through endoscopy (removal of kidney or ureter stones).
• Scars from passing stones spontaneously.
• Scarring due to radiation treatment of a tumor in the abdomen.
• Inflammation, tumors in the ureter (see SBS of the renal pelvis p. 282).
Therapy
Regular monitoring of kidney function. If the kidney is congested for a long time and the blood values worsen, i.e., nothing helps, surgery (different possible options) is worth considering.
• Renal colic: warmth, physical exercise, muscle relaxing agents, painkillers; drink sufficient pure, “soft“ water.
• Food: alkaline diet (see p. 65), especially celery, carrots, cucumbers, squash, asparagus, strawberries, beans.
• Teas: nettle, goldenrod, birch leaf, fennel, speedwell, raspberry leaves, elderberry, lady‘s bedstraw, agrimony.
• Juniper berry treatment according to Kneipp: Begin with four berries per day; afterwards, for nine days, take one more each day. Then go back to four.
• Hildegard: elixir of absinthe, fennel mixed powder.
• Massage the kidney area with camphor oil; reflex, zone massage.
• Hot baths, sauna treatments.
• Always be sure to keep the feet warm; possibly hot foot baths.
• Natural borax.
• MMS (see p. 68).
• Kanne Bread Drink.
• Zeolite powder internally.
• The best time for kidney treatments: 5 to 7 p.m.
All experience reports on the organ system “Kidneys and Ureters” from the International Report Archive:



